BECE 2013 Integrated Science Objective Questions and Answers
Answer all questions in this section.
Each question is followed by four options lettered A to D. Find the correct answer for each question.
1. The S.I unit of temperature is
Solution: The S.I unit for temperature is kelvin, used in scientific measurements.
2. Air is an example of
Solution: Air is a mixture of gases like nitrogen, oxygen, and others.
3. Which of the following activities are involved in the rearing of tilapia?
I. Feeding of fish
II. Pond stocking
III. Pest control
Solution: Tilapia rearing involves feeding, stocking ponds, and controlling pests.
4. The part of the flower that contains nectar is called
Solution: Petals often contain nectar to attract pollinators.
5. Which of the following methods protects pure iron from rusting by coating with zinc?
Solution: Galvanizing involves coating iron with zinc to prevent rust.
6. Leaching of nutrients from the soil leads to soil
Solution: Leaching removes nutrients, often increasing soil acidity.
7. The hereditary material that is passed on from parents to offspring is known as
Solution: Genes carry hereditary information from parents to offspring.
8. The solar system is made up of the
Solution: The solar system includes the sun, planets, and other celestial bodies.
9. The type of management system which allows farm animals to roam about freely is known as
Solution: Extensive systems allow animals to roam freely over large areas.
10. External respiration in living organisms is also known as
Solution: External respiration involves gas exchange, often called gaseous respiration.
11. A rigid bar which is capable of turning about a fixed point is a / an
Solution: A lever is a rigid bar that pivots around a fixed point (fulcrum).
12. A positively charged ion is called
Solution: A cation is a positively charged ion.
13. One way of ensuring that organisms are not endangered is to
Solution: Protecting habitats helps prevent species endangerment.
14. A good thermometric liquid must
Solution: A thermometric liquid should expand uniformly for accurate measurements.
15. Which of the following metals will produce a gas when placed in lime juice?
Solution: Magnesium reacts with acids in lime juice to produce hydrogen gas.
16. The physical property of a soil which is determined by the feel method is soil
Solution: Soil texture is assessed by its feel (e.g., sandy, clayey).
17. The reason why gaps are left in the joints of railway lines is to allow for
Solution: Gaps allow railway lines to expand in heat, preventing buckling.
18. Which of the following effects are caused by rusting?
I. Loss of strength
II. Loss of structure
III. Loss of electrical conductivity
Solution: Rusting weakens metals, alters structure, and reduces conductivity.
19. Leguminous crops may often be cultivated to add
Solution: Leguminous crops fix nitrogen in the soil via root nodules.
20. A place where an organism can live and interbreed successfully is called
Solution: A habitat is where an organism lives and reproduces.
21. Which of the following methods of treating water makes it soft?
Solution: Sodium carbonate removes hardness by precipitating calcium/magnesium ions.
22. Dehusking and shelling are both activities carried out in the processing of
Solution: Groundnuts require dehusking and shelling to access the edible part.
23. Typhoid fever is transmitted through
Solution: Typhoid is spread via contaminated food or water.
24. One advantage of friction is that it
Solution: Friction allows sharpening of tools by grinding surfaces.
25. Sickle is a farm tool used for
Solution: A sickle is used to cut crops like rice during harvest.
26. One characteristic of the image formed in a pin-hole camera is that the image is
Solution: Pin-hole cameras produce a diminished, inverted real image.
27. Transplanting of seedlings is usually done in the evening because
Solution: Evening transplanting reduces transpiration due to lower temperatures.
28. Which of the following statements about molecules is/are correct? Molecules
I. are chemically combined group of atoms
II. are physically combined group of atoms
III. can exist on their own
Solution: Molecules are chemically bonded atoms (I) and can exist independently (III).
29. Fruits which are dispersed by wind are likely to be
Solution: Wind-dispersed fruits often have hairy structures for easy dispersal.
30. Which of the following materials allows electric current to pass through easily?
Solution: Aluminium is a good conductor of electricity.
31. Water contains two elements, hydrogen and oxygen, in the ratio of
Solution: Water (H₂O) has a hydrogen-to-oxygen ratio of 2:1.
32. In the digestive system of ruminants, vitamins are synthesized in the
Solution: The rumen hosts microbes that synthesize vitamins.
33. The best way of protecting oneself from high blood pressure is to
Solution: Regular exercise helps maintain healthy blood pressure.
34. The property of metals which makes them to be easily drawn into thin wires is known as
Solution: Ductility allows metals to be drawn into wires.
35. An atom of an element is represented as \({}_{13}^{27} \mathbf{X}\) . How many neutrons are in the nucleus of the atom?
Solution: Neutrons = mass number (27) - atomic number (13) = 14.
36. Viable seeds are ones that
Solution: Viable seeds can germinate under favorable conditions.
37. Which of the following processes can occur at all temperatures?
Solution: Evaporation occurs at any temperature, unlike boiling.
38. Which of the following human activities maintains the carbon cycle?
Solution: Replanting trees absorbs CO₂, maintaining the carbon cycle.
39. The farming system which involves the growing of one type of crop on the same piece of land every season is known as
Solution: Monocropping involves growing one crop repeatedly.
40. The presence of chlorophyll in green plants is a necessary condition for photosynthesis because it
Solution: Chlorophyll absorbs sunlight for photosynthesis.
1. (a) The diagrams below are illustrations of an experiment to demonstrate a biological principle. Study the diagrams carefully and answer the questions that follow.
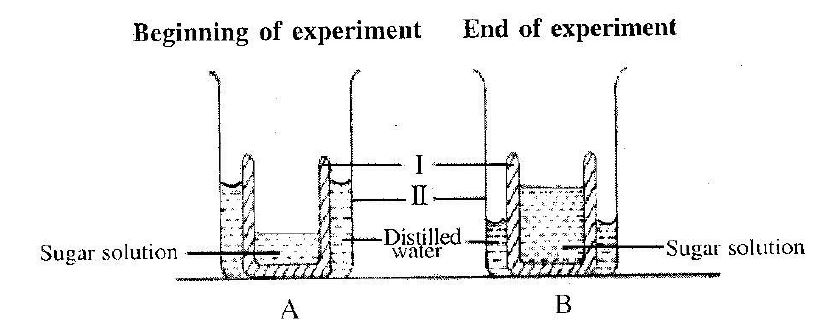
(i) Name the parts labelled I and II.
(v) State one way in which plants benefit from the principle named in (iv).
(b) In an experiment to investigate the reactivity of zinc, a piece of the metal was dropped into a test tube containing dilute hydrochloric acid. The experimental set-up is illustrated below. Study the set-up carefully and answer the questions that follow.
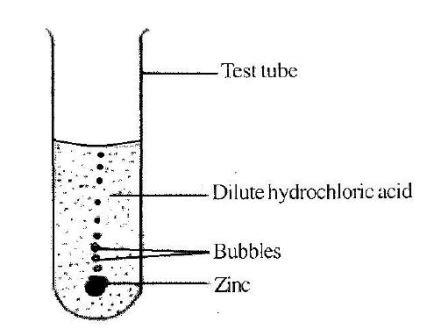
(i) Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction that occurred in the experiment.
(v) Name two glass apparatus which could have been used instead of the test tube.
(c) The diagram below is an illustration of a thermos flask. Study the diagram carefully and answer the questions that follow.
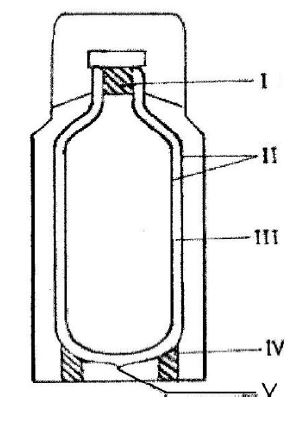
(i) Name the parts labelled I, II, III, IV, and V.
(d) The diagrams below illustrate an experimental set-up on a physical property of soil using three soil types, X,Y and Z. Study the set-up carefully and answer the questions that follow.
(i) Name the parts of the set-up labelled I, II, III, and IV.
Solutions for Question 1
(a)
(i) I: A hollow yam or potato or pawpaw cup or semi-permeable container
II: A beaker or trough
(ii) Differences between set-ups A and B:
- The sugar solution is concentrated in set-up A, while it is dilute in set-up B.
- The level of the distilled water is high in set-up A, while it is low in set-up B.
- The amount of sugar solution is smaller in set-up A, while it is greater in set-up B.
(iii) Role played by part I:
It serves as a semi-permeable membrane to allow the movement of water molecules from the water into the sugar solution.
(iv) Biological principle demonstrated:
Osmosis
(v) How plants benefit from osmosis:
- Absorption of water by the roots of plants
- Transportation of water from the roots to the other parts of the plant
- Movement of water from one plant cell to the other
(vi) How animals benefit from osmosis:
- Movement of water into the cytoplasm of some organisms such as amoeba
- Re-absorption of water in the kidney tubules of mammals
(b)
(i) Balanced equation for the reaction:
Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl₂ + H₂
(ii) The gas evolved:
Hydrogen gas or H₂ (gas)
(iii) Metals that can react in a similar way as zinc:
Lithium, Magnesium, Potassium, Sodium, Calcium, Aluminium, Iron
(iv) Metals that cannot react in a similar way as zinc:
Copper, Silver, Gold, Mercury, Platinum
(v) Glass apparatus that could have been used:
Beaker, Conical flask, Measuring cylinder, Flat-bottomed flask, Gas jar
(c)
(i) Parts:
I: Cork or plastic/rubber stopper
II: Silvered or shiny surfaced double wall
III: Vacuum or empty space
IV: Cork support or plastic/rubber support
V: Vacuum seal
(ii) How the device minimizes heat loss or gain through:
(α) Conduction: Minimized by the cork or plastic/rubber stopper and cork support or plastic/rubber support.
(β) Convection: Minimized by the vacuum.
(γ) Radiation: Minimized by the silvered or shiny surfaced double wall.
(iii) Use of the thermos flask:
- Maintains the temperature of its contents for a relatively long time, i.e., it keeps its hot contents hot and its cold contents cold.
- It prevents heat loss or heat gain of its contents for a long period.
(d)
(i) Parts:
I: Funnel
II: Cotton wool
III: Measuring cylinder
IV: Water
(ii)
(α) Highest water holding capacity: Z
(β) Least water holding capacity: X
(iii) Soil types:
X: Sandy
Y: Loamy
Z: Clayey
(iv) Suitable title for experiment:
- Experiment to compare the water-holding capacities of sandy, loamy, and clayey soils
- Experiment to demonstrate the drainage abilities of sandy, loamy, and clayey soils
2. (a) List the three particles which make up matter.
(b) State four hereditary features in humans.
(c) State the energy transformation that takes place in each of the following activities:
(i) dry cell in use;
(ii) solar panel in use;
(iii) electric stove in use;
(iv) hammering of a piece of metal
(d)State two ways each in which each of the following cultural practices is important in vegetable production:
(i) staking
pruning
Solutions for Question 2
(a) Particles which make up matter:
Protons, Neutrons, Electrons Dot
Electrons
(b) Hereditary features in humans:
Shape of nose
Size of ear
Height
Colour of skin
Mass
Colour of eyes
Temperament
Intelligence
(c) Energy transformations in the following activities:
(i) Dry cell in use: Chemical energy → electrical energy
(ii) Solar panel in use: Solar / Light energy → electrical energy
(iii) Electric stove in use: Electrical energy → heat energy + light energy
(iv) Hammering of a piece of metal: Kinetic energy → sound energy + light energy
(d) Importance of the following cultural practices in vegetable production:
(i) Staking:
- Gives the plants the ability to grow without bending or breaking
- Prevents fruits from getting rotten (as they lie on the ground)
- Enables the plant to get sufficient sunlight needed for healthy growth
- Creates space in-between plants for easier movement of the farmer
(ii) Pruning:
- Increases the quality and quantity of crop yield
- Helps to check the spread of pest and diseases
- Enables the plant to get sufficient sunlight needed for healthy growth
- Enhances healthier growth of the plant
- Improves ventilation for the plant
3. (a)
(i) What is indiscriminate sex?
(ii) Give two reasons why teenagers indulge in indiscriminate sex
(b) Name two sources each of
(i) natural light
(ii) artificial light
(c) State three ways in which soil texture is important in crop production.
(d) Write down the systematic name of each of the following chemical compounds:
(i) FeS
(ii) CO
(iii) Cu2O
(iv) NaOH
Solutions for Question 3
(a)
(i) Indiscriminate sex:
Having sexual intercourse with multiple (two or more) partners and usually without protection (use of condom).
(ii) Reasons why teenagers indulge in indiscriminate sex:
- Curiosity
- Peer pressure
- Poverty
- Illiteracy or ignorance of consequences
- Lack of sufficient recreational avenues
- Broken homes
- Irresponsible parenting
- Low self-esteem
- Fallen moral standards of society
- Lack of self-control
(b) Sources of:
(i) Natural light:
- Sun
- Stars
- Lightning
- Volcanic eruption
- Firefly
- Glow worm
- Anglerfish
- Lanternfish
(ii) Artificial light:
- Moon
- Electric bulb
- Torch
- Matches
- Vehicle headlamps
- Light-emitting diodes (LEDs)
- Light-emitting electrochemical cells (LECs)
(c) Ways in which soil texture is important in crop production:
It affects soil fertility
It affects its water-holding capacity
It affects its nutrient retention
It affects its plant-holding capacity
It affects the ability of the soil to resist erosion
It affects soil temperature
(d) Systematic name of the following chemical compounds:
(i) FeS: Iron (II) sulphide
(ii) CO: Carbon (II) oxide or Carbon monoxide (preferred IUPAC name)
(iii) Cu₂O: Copper (I) oxide
(iv) NaOH: Sodium hydroxide
4. (a)
(i) What do the symbols L, N, and E represent in an electric plug?
(b) Mention four classes of insect pest based on their feeding habits.
(c) Classify the first four elements of the periodic table as metals and non-metals.
(d) Name the three types of blood vessels in humans.
Solutions for Question 4
(a)
(i) What the symbols L, N, and E represent in an electric plug:
L: Live pin
N: Neutral pin
E: Earth pin
(ii) The function of the fuse box in household electrical wiring:
- The fuse box houses and controls the incoming electrical service and distribution to circuits within the house.
- It provides protection against power fluctuation through the use of fuses.
(b) Four classes of insect pest based on their feeding habits:
Piercing & sucking insects (e.g., aphids, mosquitoes)
Chewing insects (e.g., grasshoppers, beetles, weevils)
Siphoning insects (e.g., moths, butterflies)
Sponging insects (e.g., housefly)
(c) Classification of the first four elements of the periodic table:
(d) The three types of blood vessels in humans:
Capillaries
Veins
Arteries
5. (a)
(i) State the difference between organic fertilizer and inorganic fertilizer.
(ii)State two effects of inorganic fertilizer on the environment
(b) Classify the following substances as acids or bases:
(i)unripe lemon juice
(ii) wood ash
(iii) liquid in a car battery
(iv) bicarbonate of soda
(c)
(i)What is a fruit?
(ii) State two differences between a fruit and a seed.
(d) State the effect of heat on each of the following substances:
(i) plastics
(ii) alcohol
(iii) metal rod
Solutions for Question 5
(a)
(i) Difference between organic fertilizer and inorganic fertilizer:
| organic fertilizer | inorganic fertilizer | Made from animal or plant matter (natural sources) | Made from chemicals (artificial sources) |
|---|
(ii) Effects of inorganic fertilizer on the environment:
- Damage and destruction of plant and animal life, when used in excess
- Contamination of water bodies when rain washes chemicals into them
- Contributes to the formation of acid rain, when fossil fuels are burnt during their production
- Contributes to the greenhouse effect, when fossil fuels are burnt during their production
- Nitrogen-containing fertilizers can cause soil acidification
(b) Classification of the following substances as acids or bases:
(c)
(i) A fruit:
A mature ovary containing seed
(ii) Differences between a fruit and a seed:
| FRUIT | SEED | A mature ovary | A mature ovule |
|---|---|
| Contains a seed | Contains an embryo | Pericarp is formed from the wall of the ripened ovary | The seed coat (testa) is formed from integuments of ovule |
| Cannot germinate under any condition | Can germinate under the right conditions |
(d) The effect of heat on each of the following substances:
(i) Plastics: Causes melting
(ii) Alcohol: Causes boiling or faster evaporation
(iii) Metal rod: Causes expansion
6.
(a)
Classify the following chemical substances based on their uses under the headings Agriculture, Industry, Medicine:
Milk of magnesia, alcohol, paracetamol, sodium hydroxide, N.P.K
(b) State one use each of the following instruments used in the study of the weather:
(i) rain gauge
(ii) hygrometer;
(iii) anemometer.
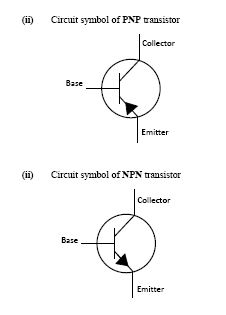
(c)(i) Name two types of transistors.
(ii) Draw and label the circuit symbols of the transistors named in (i)
(d)State three reasons why vegetable farming is important.
Solutions for Question 6
(a) Classification of: Agriculture: N.P.K. Industry: alcohol, sodium hydroxide Medicine: Milk of magnesia, paracetamol
(b) One use each of the following instruments:
(i) Rain gauge: To measure the amount of rainfall
(ii) Hygrometer: To measure the atmospheric humidity
(iii) Anemometer: To measure the speed of wind
(c)
(i) Types of transistors:
- PNP transistor
- NPN transistor
(ii) Circuit symbols:
(d) Reasons why vegetable farming is important:
Source of employment - Income generation or wealth creation
Foreign exchange earner for the nation, when exported
Provision of nutrition for man - Vegetables are very rich in essential vitamins, mineral salts, and proteins
Certain vegetables help to conserve soil fertility
Provides raw material for the food processing industry
Certain vegetables are used in the pharmaceutical industry
Vegetables take a shorter time to mature, hence provide greater returns per given time and space